AgroTech project as an example of how CREODIAS can be used for food and environmental research
CloudFerro together with the QED Software team is working on a Research & Development project AgroTech to test and review its cloud capabilities for agriculture-related applications. After 1 year of collaboration on the project, we would like to share our main thoughts about implementing solutions for agriculture on CREODIAS.
EXTRACTING LAND INFORMATION FROM EARTH OBSERVATION DATA
One of the land cover aspects is the possibility of extracting its types, density, or frequency from Earth observation. Conscious land management requires a trustworthy source of current data. Land cover and land use classification is the most common basic source of information for the Earth's surface. Satellite imagery creates an opportunity to see the land surface in plenty of various bands and with wide radiometric resolution. Therefore, thematic aggregation is needed. Classification is used for simplifying the content as well as reducing the weight of data.
There are plenty of available methods and solutions for providing such information. CREODIAS users can conduct their own classification or choose from widely available ready thematic layers e.g., S2GLC or Copernicus High-Resolution Layers available on the CREODIAS EO data cloud repository. However, these methods have their limitations starting from chosen methodology and timeframe and ending with imperfect accuracy. They are great for general analysis on a wide scale of Europe, but when it comes to details, they seem insufficient.
AGROTECH AS A GOOD EXAMPLE
Looking at our users’ demands and needs, CloudFerro has started a research and development project AgroTech to test and review our cloud capabilities in order to provide the best possible environment for:creating new methodsconvenient gaining from existing thematic layersgenerating on-demand dedicated productsefficient use of cloud infrastructuretesting various settings and properties of Virtual machines suitable for user algorithms
AgroTech not only aims at creating innovative tools and information for CREODIAS users to incorporate in their value chains – ready-to-use classification models ranging from land cover to crop type and status classification and tools to train and retrain new networks. It also allows CloudFerro to evaluate and optimize its services. New capabilities will be offered both as containerized applications executed by PGaaS workflows – which require less configuration on the users’ side - and as new VM (Virtual Machine) images for the users to choose from.
Combining existing CREODIAS PGaaS and VM-based processing capabilities with Copernicus data repository and AgroTech results will further simplify generating added value from satellite imagery for the agriculture sector and beyond. Thus, it enables more stakeholders to participate in the market and promotes the uptake of Copernicus-born data throughout European industries.
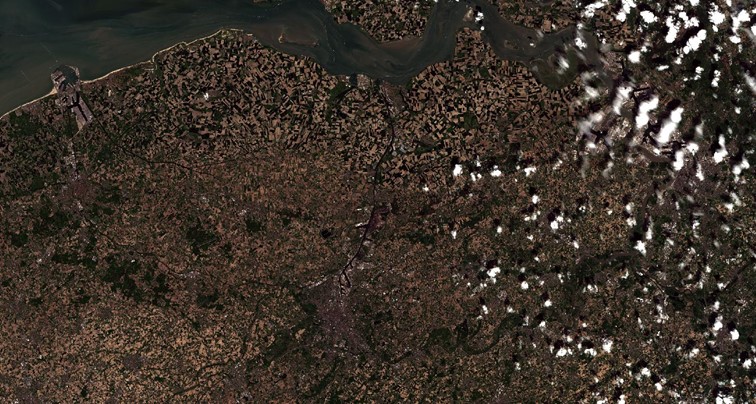
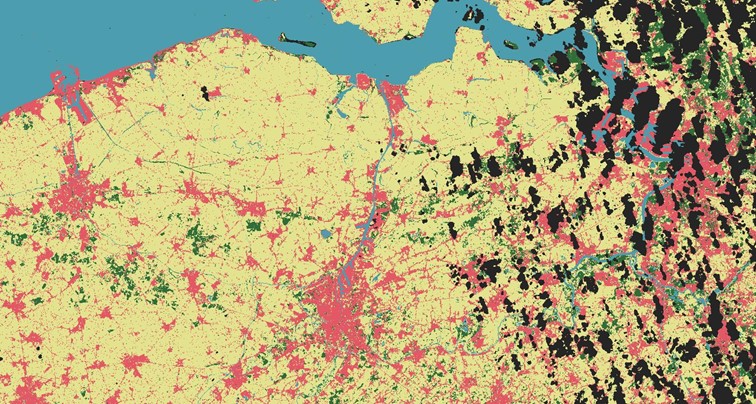
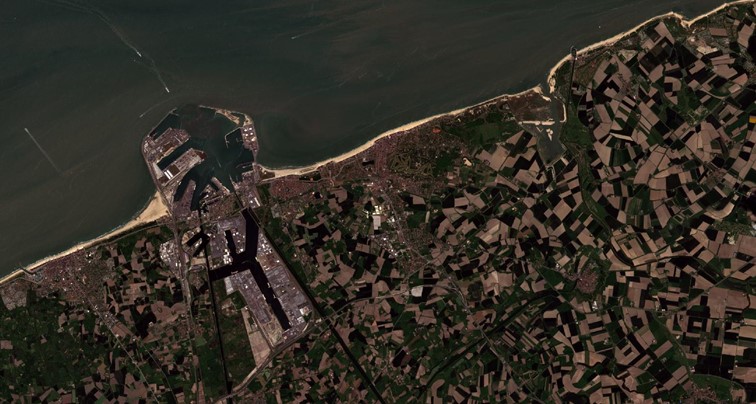
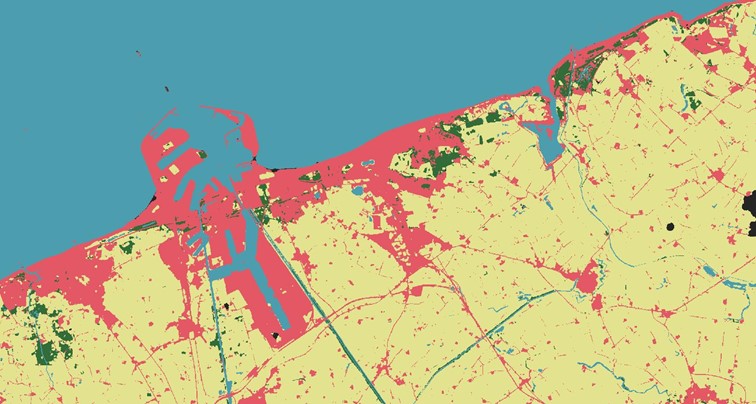
Below you can find examples of conducted land cover classification as part of the AgroTech project for northern Belgium and the southern Netherlands.
Use the arrows and swipe to compare the images of different classification - southern Netherlands


Use the arrows and swipe to compare the images of different classification - northern Belgium

AGRICULTURE IN A GLOBAL APPROACH
Leveraging the existing system with big ambitions allows us to turn them into everyday realities. Global scaling requires an unlimited data repository and scalable IT infrastructure. Global ideas therefore could be achieved with a global tool such as CREODIAS. Cloud technologies enable things not possible ever before with their scale limitations.
AGRICULTURAL DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
CREODIAS aims to empower the digital transformation which is taking place in agriculture. Any agricultural project outcome fully implemented in our infrastructure will contribute to and encourage implementing a more resilient food system.
CREODIAS CREDIBILITY AND UTILITY FOR AGRO SOLUTION MARKET
Food security nowadays is a burning issue. Facing new challenges in a dynamically changing world requires elasticity, speed, and efficiency. Therefore, CREODIAS cloud infrastructure is a perfect environment to conduct any big data initiative supporting agriculture, where the need for smart Earth Observation techniques increases with the growing uncertainty of food chain safety.
Authors: Sylwia Nasiłowska (PhD), R&D Project Manager at CloudFerro, and Stanisław Krzyżanowski, Business Development Manager at CloudFerro

